The role of aluminum foil in the new energy field has upgraded from an auxiliary material to a core supporting material, deeply supporting the performance upgrading and large-scale development of power batteries, energy storage, photovoltaic and other industries. Its functions focus on core needs such as electrical conduction, carrier and protection, and continue to expand with technological iteration. In the future, with the continuous expansion of the new energy industry, continuous technological breakthroughs and the advancement of the “dual carbon” goal, aluminum foil will continue to upgrade towards ultra-thinness, high strength, composite and greenization, with steady expansion of market scale and continuous optimization of industry pattern. It will become an important support for the high-quality development of the new energy industry, and at the same time usher in a structural leap of its own industry.
The Core Role of Aluminum Foil in the New Energy Field
The application of aluminum foil in the new energy field is concentrated in the energy storage and conversion links, among which power batteries and energy storage batteries are the core demand scenarios, and it also plays an auxiliary supporting role in photovoltaic, wind power and other fields. Its role in different scenarios focuses on the three core goals of performance improvement, safety guarantee and cost control.
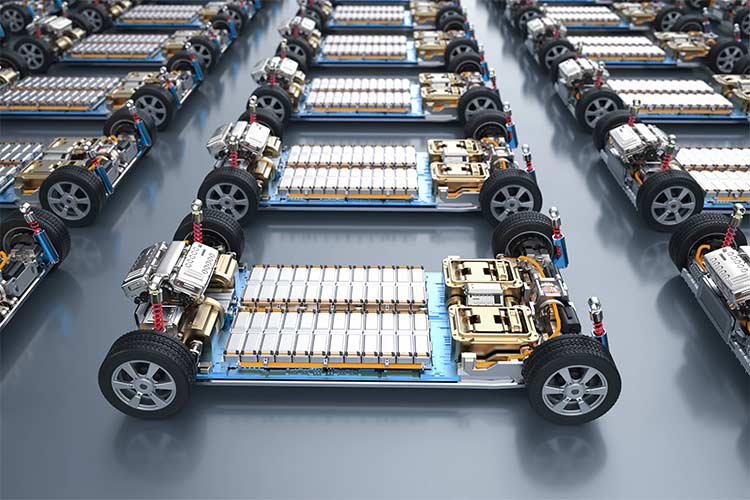
(I) Power Battery Field: An Indispensable Core Current Collector and Functional Material
Power batteries are the largest demand market for aluminum foil in the new energy field. Its dosage and performance directly determine the energy density, cycle life and safety performance of batteries. The core application is the positive electrode current collector, and at the same time, it derives multi-functional variants such as carbon-coated and composite materials.
1. Core Function of Positive Electrode Current Collector: As a carrier for the active material of the positive electrode of lithium batteries, aluminum foil can quickly conduct the electrons generated during the charging and discharging process of the battery with its excellent electrical conductivity, reducing energy loss; at the same time, its good ductility and corrosion resistance can adapt to the rolling, cutting and other processing technologies of battery pole pieces, bear the mechanical stress during battery assembly and cycling, and avoid the short-circuit risk caused by pole piece damage. At present, in the liquid lithium battery system, aluminum foil has achieved stable supply, and it is one of the core supporting materials for mass production of power batteries. The dosage of aluminum foil per gigawatt of lithium batteries can reach 600-800 tons.
2. Function Upgrade and Expansion: With the upgrading of power batteries towards high energy density and high safety, special products such as carbon-coated aluminum foil and composite aluminum foil have gradually become popular. Carbon-coated aluminum foil can reduce battery internal resistance, improve the adhesion of active materials, and improve battery cycle performance, and has begun to expand to sodium-ion batteries and solid-state batteries; composite aluminum foil (such as 6-micron PET plus 2-micron aluminum layer structure) can achieve significant weight reduction, reducing battery mass by nearly 58% and increasing energy density by about 4.2%, perfectly adapting to the lightweight demand of new energy vehicles, and at the same time having outstanding advantages in safety, which has entered the mass production stage.
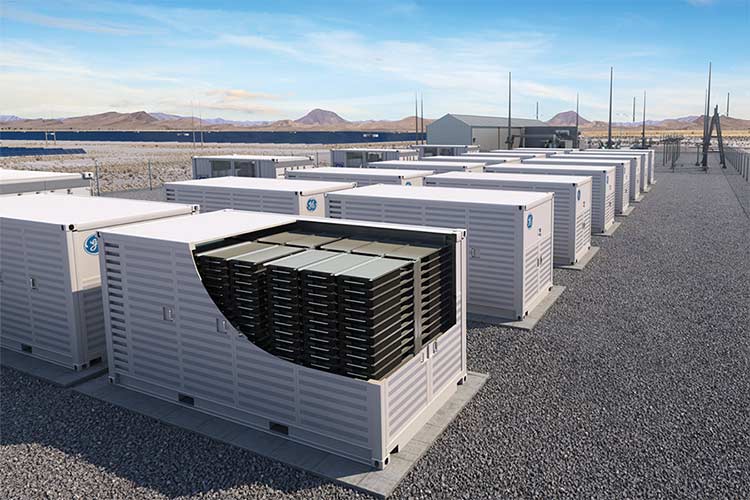

(II) Energy Storage Battery Field: A Low-Cost Adaptive Material for Large-Scale Storage
The explosive growth of the global energy storage industry has driven the rapid release of demand for aluminum foil for energy storage batteries. Its core role is to achieve cost optimization on the premise of ensuring the safety and long cycle life of energy storage, adapting to the batch application of large-scale energy storage scenarios. The technical route of energy storage batteries is highly homologous to that of power batteries. Aluminum foil also plays the role of electrical conduction and carrier as the positive electrode current collector. Moreover, because energy storage batteries have lower requirements on lightweight than new energy vehicles, they focus on cost performance advantages. At present, the demand for aluminum foil in the energy storage battery field has accounted for 18%, and the demand growth rate will continue to increase with the expansion of energy storage installed capacity in the future.
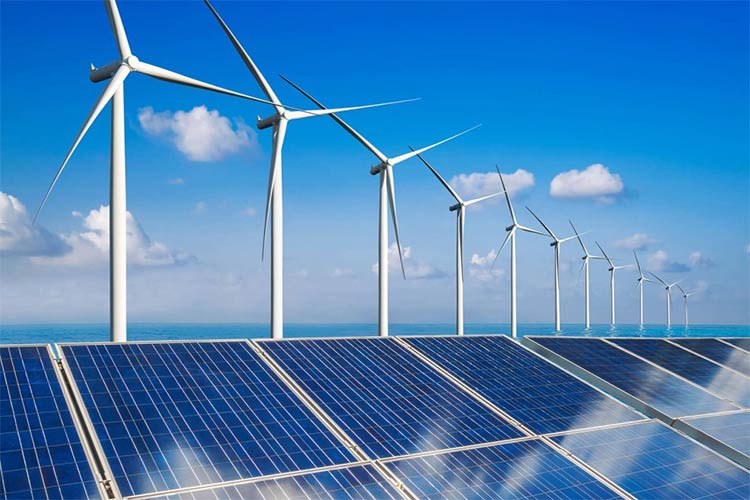

(III) Photovoltaic and Wind Power Fields: Auxiliary Supporting and Protective Materials
In the photovoltaic field, aluminum foil is mainly used for the packaging and heat dissipation of photovoltaic inverters and photovoltaic modules. Its excellent thermal conductivity can accelerate the heat dissipation speed of electronic components inside the inverter, avoid overheating and aging of components, and extend the service life of the photovoltaic system; at the same time, the barrier property of aluminum foil can be used as the moisture-proof layer of the back sheet of photovoltaic modules to prevent component failure caused by water vapor penetration. In the wind power field, aluminum foil is mainly used for cable wrapping and internal protection of the engine room of wind turbines. It uses its barrier properties and corrosion resistance to protect cables from external environmental erosion and ensure the stable operation of the power generation system.
(IV) Other New Energy Scenarios: Functional Extension and Supporting Support
In the field of new energy charging facilities, aluminum foil is used for insulation and heat dissipation wrapping of internal lines of charging piles to improve the operation stability of charging piles; in the hydrogen energy field (hydrogen energy as a supplementary path for new energy), aluminum foil can be used for sealing and barrier components of hydrogen fuel cells, using its compactness to prevent hydrogen leakage and ensure the safe operation of batteries.
